今年的AP大考已经开启了100天倒计时,相信不少同学已经进入了新课吸收与复习同步进行的状态。本文就来给大家精讲一下4个非常重要的AP心理学知识点(中英文双语)——斯金纳箱实验、奖罚分明、延迟满足、奖励频率。既可以用来预习,也可以作为复习资料补充。

心理学是一门综合国际课程,值得一提的是文科和理科学员都很适合复习。
AP心理学考试包含两大部分,共120分钟。
(1)多选题(70min),共100个问题,分值占总分的三分之二。
(2)开放性问题(50min),共两大题,分值占总分的三分之一。
AP心理学作为给国际学校生的预修课程,讲述的都是心理学的入门知识。其中包括心理学的理论,概念及运行方式。
Operant Conditioning 操作性条件反射:个体产生自愿行为(Skinner & Thorndike)(Behaviorism)
a) ThorndikeàInstrumental Learning 桑代克à工具性学习
-S-R Connection 刺激-反应链接:行为的形成仅仅是刺激和反应连接的结果;结果好,连接加强;结果不好,连接减弱。
b) B. F. Skinnerà Operant Conditioning 斯金纳à操作性条件反射
-Reinforcement 强化:增加行为频率
1)Positive Reinforcement 正强化:增加对象喜爱的刺激,行为频率增加
2)Continuous Reinforcement 连续强化:每次当理想行为出现时,都给予强化,可以快速学习新的行为,但是消失得也很快。
3)Negative Reinforcement 负强化:减少对象厌恶的刺激,行为频率增加
-Escape Learning 逃避学习:使得对象结束其厌恶的刺激
-Avoidance Learning 回避学习:使得对象避免接触厌恶的刺激
-Punishment 惩罚:减少行为频率(比强化有效)
1)Positive Punishment正惩罚:加强对象厌恶的刺激,行为频率减少
2)Negative Punishment负惩罚:减少对象喜爱的刺激,行为频率减少
-Omission Training 忽视训练
-Skinner Box 斯金纳箱
1)一只小白鼠禁食24小时后被放入箱内(在箱内按一下按钮,即有一粒食物从小孔口落入小盒内)
2)小白鼠偶尔按压按钮获得食物(positive reinforcement);重复若干次后形成了压杆取食的条件反射
-Shaping 行为塑造:独立行为作为一个塑造单位,每个行为完成后给予奖励
-Chaining 链接:训练一系列连续的独立行为,在所有完成后再给予奖励
3)Reinforcer 强化物
-Primary Reinforcers 初级强化物:无需学习就可强化的刺激,基本生理需求,例如食物
-Secondary Reinforcers/Conditioned Reinforcers 二级强化物:需要学习才能被强化的刺激,比如金钱
3. Schedules of Reinforcement 强化的不同模式
a) Fixed-Ratio Schedule 固定比率程序:强化物在有机体做出一定数目的反应后才出现,比如每10次行为就给一次奖励
b) Fixed-Interval Schedule 固定间隔程序:强化物在经过一个确定的时间间隔后加入,效率最低,比如每隔十分钟给一次奖励
c)Variable-Ratio Schedule 变化比率程序:平均反应次数预先确定,强化物在平均反应次数出现时才出现,但是反应次数不一定,效率最高,例如平均每十次行为给一次奖励,但是每次奖励可能会在五次行为或者是N次行为的时候出现。
d)Variable-Interval Schedule 变化间隔程序:平均时间间隔预先确定,强化物在平均时间间隔出现后加入,时间不固定,比如平均每隔十秒给一次奖励,但是具体每次奖励都会搁置N秒(不确定秒数)。
e)Continuous 连续强化:对于形成新的行为非常重要,如果每次都得到强化,新的行为很容易快速建立起来
请注意:变化程序比固定程序更能够抵抗消退反应(Vs are more resistant to extinction.)
4. Biology and Operant Conditioning 生物学意义上的学习
a) Instinctive Drift 本能漂移:机体在习得某种行为之后恢复本能行为的趋势,这种习得并不稳定,在环境改变之时,行为会自动倾向本能。
接下来,就让我们一起看看英文版的AP心理学知识点讲解吧。
1.Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher.
operant conditioning与classical conditioning的差异:
Classical conditioning and operant conditioning are both forms of associative learning, yet their difference is straightforward.
1) Classical conditioning forms associations between stimuli (a CS and the Us it signals).
It also involves respondent behavior—actions that are automatic responses to a stimulus (such as salivating in response to meat powder and later in response to a tone)
重点:classical conditioning 是自动的,天然的
2) In Operant conditioning, organisms associate their own actions with consequences. Actions followed by reinforcers increases; those followed by punishers often decrease.
Behavior that operates on the environment to produce rewarding or punishing stimuli is called operant behavior.
重点: operant conditioning 重在结果,奖罚分明
2. B. F. Skinner’s Experiments
*实验是以law of effect (Edward L. Thorndike)为基础展开的
Law of effect is Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and that behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely.
Law of effect: rewarded behavior is likely to recur.
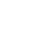
-Skinner designed an operant chamber, popularly known as a Skinner box. (如上图)
*Operant chamber: in operant conditioning research, a chamber (also known as a Skinner box) containing a bar or key that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer; attached devices record the animal’s rate of bar pressing or key pecking.
--reinforcement: any event that strengthens (increase the frequency of) a preceding response. // in operant conditioning, reinforcement is any event that strengthens the behavior it follows.
(not only teach us how to pull habits out of a rat, but also explore the precise conditions that foster efficient and enduring learning)
--shaping behavior: shaping means gradually guiding the rat’s actions toward the desired behavior.
*shaping is an operant conditioning procedure in which reinforcers guide behavior toward closer and closer approximations of the desired behavior. [approximations: rewarding the small steps toward learning a whole new behavior]
*With this method of successive approximations, you reward responses that are ever-closer to the final desired behavior, and you ignore all other responses.
--discriminative stimulus: in operant conditioning, a stimulus that elicits a response after association with reinforcement (in contrast to related stimuli not associated with reinforcement)
--reinforcement is any consequence that strengthens behavior.
Sometimes negative and positive reinforcement coincide. Imagine a worried student who, after goofing off and getting a bad test grade, studies harder for the next test. This increased effort may be negatively reinforced by reduced anxiety, and positively reinforced by a better grade. Whether it works by reducing something aversive, or desirable, reinforcement is any consequence that strengthens behavior,
--positive reinforcement: increasing behaviors by presenting positive reinforcers. A positive reinforcer is any stimulus that, when presented after a response, strengthens the response.
Positive reinforcement strengthens a response by presenting a typically pleasurable stimulus after a response.

(e.g., a teacher who pastes gold stars on a wall chart beside the names of children scoring 100 percent on spelling tests. The teacher would be better advised to apply the principles of operant conditioning—to reinforce all spellers for gradual improvements/ successive approximations toward perfect spelling of words they find challenging) 举个例子:导师奖励100分的学员小红花/小星星
--negative reinforcement: increasing behaviors by stopping or reducing negative stimuli. Negative reinforcement strengthens a response by reducing or removing something negative. A negative reinforcer is any stimulus that, when removed after a response, strengthens the response.
重点注意了:Negative reinforcement is not punishment. 【negative rein
forcement removes a punishing/aversive event, e.g., negative reinforcement=something that provides relief, such as bad headache, annoying alarm】
(e.g., taking aspirin may relieve your headache, and pushing the snooze button will silence your annoying alarm. These welcome results provide negative reinforcement and increase the odds that you will repeat these behaviors).
--primary reinforcer is an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need. (e.g., getting food when hungry or having a painful headache go away is innately satisfying. These primary reinforcers are unlearned. )
--conditioned reinforcers/ secondary reinforcers get their power through learned association with primary reinforcers. (p278) Conditioned reinforcer is a stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer. (e.g., money, good grades, a pleasant tone of voice)
--delay gratification延迟满足 (人类有,动物30秒后就消失) (e.g., the paycheck at the end of the week, the good grade at the end of the term, the trophy at the end of the season)
【延迟满足吃糖,今日吃小糖,坚持到明天就吃大糖,Learning to control our impulses in order to achieve more valued rewards is a big step toward maturity (Logue, 1998a,b)】 No wonder children who make such choices has tended to become socially competent and high-achieving adults (Mischel et al., 1989)
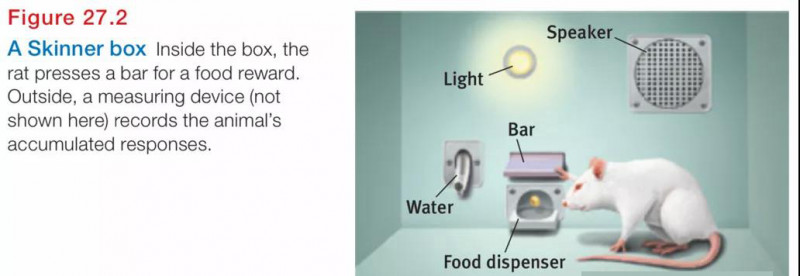
--reinforcement schedules: a pattern that defines how often a desired response will be reinforced.
1) with continuous reinforcement (reinforcing the desired response every time it occurs, learning occurs rapidly, which makes this the best choice for mastering a behavior. But extinction also occurs rapidly.
2) partial (intermittent) reinforcement means reinforcing a response only part of the time (in which responses are sometimes reinforced), which results in slower acquisition of a response but much greater resistance to extinction than does continuous reinforcement. (e.g., salespeople do not make a sale with every pitch.// gambling machines//lottery tickets)
[hope springs internal] 同样适用于child caregivers 应对小朋友们的发脾气现象。
3) fixed-ratio schedules reinforce behavior after a set number of responses.
In operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response only after a specific number of responses.
(e.g., Coffee shops may reward us with a free drink after every 10 purchased.)
4)variable-ratio schedules provide reinforcers after a seemingly unpredictable number of responses. (p280) Variable-ratio schedule in operant conditioning, a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response after an unpredictable number of responses.
(e.g., slot machine players and fly-casting anglers) Because reinforcers increase as the number of responses increases, variable-ratio schedules produce high rates of responding.
5) fixed-interval schedules reinforce the first response after a fixed time period. Fixed-interval schedule in operant conditioning, is a reinforcement that reinforces a response only after a specific time has elapses. (e.g., people check more frequently for the mail as the delivery time approaches) . 感觉快递要到了,会频繁查邮件
6) variable-interval schedules reinforce the first response after varying time intervals. Variable-interval schedule in operant conditioning, is a reinforcement schedule that reinforces a response at unpredictable time intervals. Variable-interval schedules tend to produce slow, steady responding.
--punishment
Reinforcement increases a behavior; punishment does the opposite.
A punisher is any consequence that decreases the frequency of a preceding behavior.
首先,要分清楚punishment与negative reinforcement 的区别:
Negative reinforcement encourages behavior: When something unpleasant ceases, the behavior that caused it to stop is reinforced.
Punishment discourages behavior: Behavior that is unwanted is punished, making it less likely for that behavior to continue. (e.g., a child who is burned by touching a hot stove will learn not to repeat this behavior.)
Punishment is an event that tends to decrease the behavior that it follows.
总结:Punishment tells you what not to do; reinforcement tells you what to do.
4个重要AP心理学知识点就介绍到这里,希望能帮助你把这些知识点理解得更透彻。
距离今年AP心理学只有100天出头的复习时间了,如果你想更有针对性地复习,也可以点击预约试听【唯寻AP复习冲刺班】,唯寻教学天团授课,适合所有在校考生与社会考生。提前攻克薄弱环节,从近年真题中解码考点,梳理高频知识点,一课一练形成学习闭环,扎扎实实冲刺5分。
更多AP复习攻略点击

学习有方法,成长看得见
筑梦牛剑/G5/常春藤