之前我们也给大家介绍了CIE考试局取消了英国的IGCSE考试,但是疫情稳定的国家考试还是会正常举行的。今天我们也给大家总结了一些有关IGCSE物理热学知识点,如果有需要的同学一起来看看吧!
Three state of matter
| state | size | shape |
| solid | fixed volume | fixed shape |
| liquid | fixed volume | shape of its container |
| gas | volume of its container | shape of its container |
Melting point and boiling point
melting point
A pure substance changes from solid to liquid at a fixed temperature.
boiling point
A pure substance changes from liquid to gas at a fiexed temperature.
The kinetic model
| state | arrangement of particles | movement of particles |
| solid | The particles are packed closely together | They vibrate about a fixed position |
| liquid | The particles are packed slightly less closely together compared with solid | The particles are both vibrating and moving from place to place |
| gas | The particles are widely separated from one another | The particles are moving freely about |
Brownian motion
Brownian motion is the random motion of particles suspended in a fluid (a liquid or a gas) resulting from their collision with the quick atoms or molecules in the gas or liquid.
Evaporation
The process that water has become water vapour in the air.
Why does evaporation make things cooler?
Th e particles that are escaping from the water are the fastest-moving ones. They are the particles with the most energy.
This means that the particles that remain are those with less energy, and so the water is colder.
Attractive force
It is the attractive force that hold together the particles that made up matter.
Attractive force in solid,liquid and gas
force in solid > force in liquid > force in gas
Kinetic theory and changes of state
Heat the material and eventually the particles have sufficient energy for all of the attractive forces between particles to be overcome. Thus, the state of matter is changed.
Gas exerts a pressure
High-speed molecules collide with the wall of container.
Each collision thus results in a change of momentum of the air molecule.
Each molecule that collides with the wall exerts a tiny force.
Because there are so many fast-moving particles, and because they collide so frequently with all the surfaces in the room, they exert a large force.
Boyle's law
The volume of a fi xed mass of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure, provided its temperature remains constant.
Formula
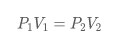
Temperature and pressure
For fixed volume of gas, when the heat increases, the pressure will increase, too.
Internal energy
Internal energy is the total energy of all of the particles.
temperature
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the individual particles.
Two fixed points
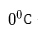 - the freezing point of pure water at atmospheric pressure,
- the freezing point of pure water at atmospheric pressure,
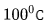 - the boiling point of pure water at atmospheric pressure.
- the boiling point of pure water at atmospheric pressure.
Linear scale
The marks on the scale are evenly spaced.
Range
The difference between highest fixed point to lowest fixed point.
Sensitivity
The degree to measure the small change of temperature.
Responsiveness
The time for liquid to reach the temperature of the surroundings.
Using thermocouple
To use the thermocouple, its ends are connected to a sensitive voltmeter.
Then one junction is placed in melting ice at 0 °C while the other is placed in the object whose temperature is to be measured.
The voltmeter shows a reading.
Advantages for thermocouple
Thermocouples can be used to measure high temperatures.
Thermocouples are useful for measuring rapidly varying temperatures.
Thermocouples can be linked to other electrical circuits or a computer.
Thermal expansion
Most substances (solids, liquids and gases) expand when they are heated.
Thermal expansion in solid, liquid and gas
| state | exapnsion |
| solid | expand more slowly when they are heated |
| liquid | generally expand faster than solids |
| gas | expand faster |
Thermal capacity
Thermal capacity is a measurable physical quantity equal to the ratio of the heat added to (or removed from) an object to the resulting temperature change.
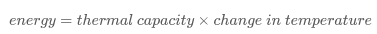
thermal capacity and materials
Metal objects heat up easily – their thermal capacities are low.
Objects made of non-metals and liquids (such as water and oil) have higher thermal capacities.
The energy required per kilogram and per degree Celsius to raise the temperature of a substance.
Formula

The energy is supplied to melt or boil a substance without raising its temperature.
Formula

specific latent heat of vaporisation
The energy per kilogram required to cause a substance to change state from liquid to gas at its boiling point.
specific latent heat of fusion
The energy per kilogram required to cause a substance to change state from solid to liquid at its melting point.
conduction
Thermal energy (heat) is transferred from the hot end to the cold end as the faster particles pass on their extra motion to particles all along the bar.
The process is called conduction.
Conductor
Materials that are good at conducting heat.
insulator
Materials that are not good at conducting heat.
Metals are good conductors
In a metal there are particles called electrons that can move about freely. Electrons carry energy when an electric current fl ows through a metal.
convection
Convective heat transfer occur between two objects separated by a moving interface of liquid or gas.
convection current
A convection current is a movement of a fl uid that carries energy from a warmer place to a cooler one.
Thernal radiaion can travel through a vacuum.
Radiation rate
All objects give out some thermal radiation.
The higher their surface temperature and the greater their surface area, the more energy they radiate per second.
emmiter and absorber
Matt black surfaces are the best absorbers and absorbers as well.
reflector
Shiny or white surfaces are the best refl ectors.
IGCSE课程的适应期的确艰难,但适应期也是让学员体验不同国际课程,帮助自己提前找到方向,及时做好调整的关键时期。适应期过渡得好,才能顺利在大考拿A*,而且还能为AL/IB选课及申请,做长线规划的准备。如果你还没有找到度过适应期的方法,如果不想在错误的方向上慢慢摸索,点击预约试听【唯寻IGCSE同步培训班】——
经验丰富的唯寻教学天团授课
根据学校进度与学员能力定制课程
大数据辅助教学
精准定位学员知识漏洞
帮助学员做好词汇能力进阶、思维转换等各项衔接准备
培养学员世界知名大学要求的学习力

如果您想了解更多,欢迎您登录唯寻国际教育官网查看。

学习有方法,成长看得见
筑梦牛剑/G5/常春藤