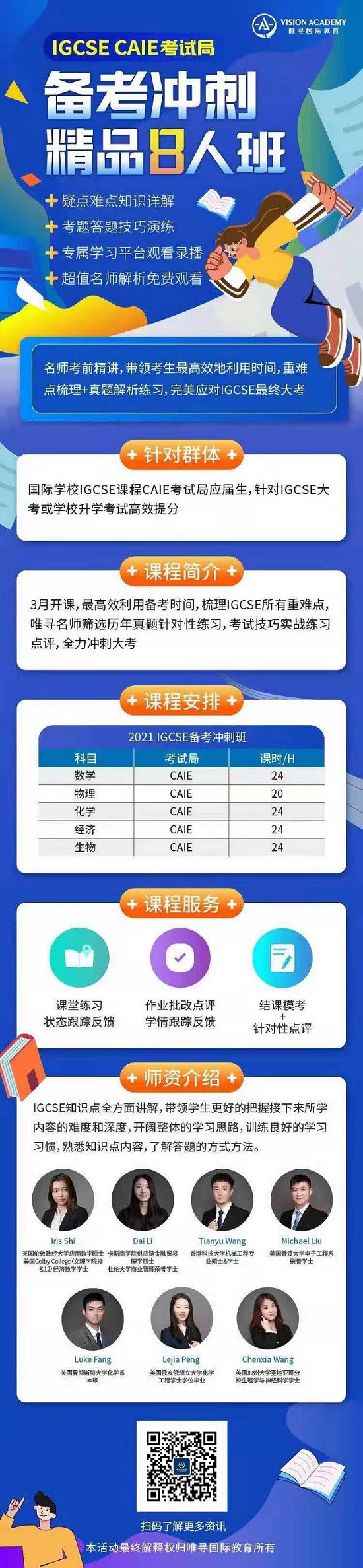
普通物理是GCSE物理考试的基础内容,本文就来给大家汇总一下普通物理相关的考点,帮助大家加快GCSE物理考试复习效率。虽然今年夏天英国本土是不考试的,但觉得导师评估分的模拟考或外部卷也要认真对待,才能助力一个高的分数去冲刺目标大学。
GCSE物理考试介绍
IGCSE物理考三张试卷。参加核心课程内容考试的同学,考试卷1、试卷3和试卷5或6。参加拓展课程内容考试的同学,考试卷2、试卷4和试卷5或6。
其中试卷1和试卷2是选择题,有40道单项选择题,考试时间为45分钟,占总分值的30%。
试卷3和试卷4是理论知识题,考试时间为1小时45分钟,满分80分,占总成绩的50%。
试卷5和6是实验知识卷,学员可根据自身情况任选其一。
GCSE物理考试难度不算大,但它检测的知识面非常的广。如果平时的基础没有打好,复习的时候可能会有点来不及。
GCSE物理考试考点整理
普通物理篇
1.1 Length and time 长度和时间
1. Use and describe the use of rules and measuring cylinders to determine a length or a volume. 使用并且描述如何用尺子和量筒测量长度和体积。
2. Use and describe the use of clocks and devices for measuring an interval of time.
使用并且描述如何用钟表和一些仪器测量时间间隔。
3. Use and describe the use of a mechanical method for the measurement of a small distance.
使用并描述利用机械的方法测量短距离。
4. Measure and describe how to measure a short interval of time (including the period of a pendulum). 测量和描述怎样测量一个短时间间隔(包括单摆的周期)。
1.2 Speed, velocity and acceleration 速率,速度,加速度
1. Define speed and calculate speed from total distance/total time.
定义速率和计算 :速率=总路程/总时间
2. Plot and interpret a speed/time graph or a distance/time graph.
画和解释 速率/时间 图像或者 路程/时间 图像
3. Recognize from the shape of a speed/time graph when a body is (a) at rest, (b) moving with constant speed, or (c) moving with changing speed.
从 速率/时间 图像中辨认出:(a) 静止,(b) 匀速运动和 (c) 变速运动。
4. Calculate the area under a speed/time graph to determine the distance traveled for motion with constant acceleration.
计算 速率/时间 图像中的面积得出匀加速运动的路程。
5. Demonstrate some understanding that acceleration is related to changing speed.
解释加速度和速度的改变量之间的联系。
6. State that the acceleration of free fall for a body near to the Earth is constant.
说明地球表面附近的物体自由降落的加速度是衡定的。
7. Distinguish between speed and velocity.
区分速率和速度。
8. Recognize linear motion for which the acceleration is constant and calculate the acceleration.
认识匀加速的运动并且计算加速度。
9. Recognize motion for which the acceleration is not constant.
认识非匀加速运动。
10. Describe qualitatively the motion of bodies falling in a uniform gravitational field with and without air resistance (including reference to terminal velocity).
定性的描述计和不计空气阻力物体在均匀重力场中下落的运动(包括设计到末速度。
1.3 Mass and weight 质量和重量
1. Show familiarity with the idea of the mass of a body.
熟练掌握一个物体的质量的概念。
2. State that weight is a force.
陈述重量是一种力。
3. Demonstrate understanding that weights (and hence masses) may be compared using a balance.
阐明重量(因此质量)可以用天平来比较。
4. Demonstrate an understanding that mass is a property which 'resists' change in motion.
阐明质量是物体阻碍加速度的一种性质
5. Describe, and use the concept of, weight as the effect of a gravitational field on a mass.
描述和利用重力是重力场作用在物体上的效果的概念。
1.4 Density 密度
1. Describe an experiment to determine the density of a liquid and of a regularly shaped solid and make the necessary calculation.
描述一个测量液体或者规则形状的固体的密度的实验并做必要的计算。
2. Describe the determination of the density of an irregularly shaped solid by the method of displacement and make the necessary calculation.
描述通过替代法测量一个不规则形状的固体的密度并做必要的计算。

1.5 Force 力
(a) Effects of forces 力的作用效果
1. State that a force may produce a change in size and shape of a body.
说明一个力可以改变一个物体的大小和形状。
2. Plot extension/load graphs and describe the associated experimental procedure.
画 伸长量/力 的图像并描述这个相关实验过程。
3. Describe the ways in which a force may change the motion of a body.
描述力可以怎样改变一个物体的运动。
4. Find the resultant of two or more forces acting along the same line.
求共线的两个或多个力的合力。
10. Interpret extension/load graphs.
解释 伸长量/负荷 的图象。
11. State Hooke’s Law and recall and use the expression F = k x.
说明胡克定律并记住使用F=kx。
12. Recognize the significance of the term 'limit of proportionality' for an extension/load graph. 从 伸长量/负荷 图像中辨认出正比例限度。
13. Recall and use the relation between force, mass and acceleration (including the direction).
记住和应用力,质量和加速度之间的关系。(F=ma)。
14. Describe, qualitatively, motion in a curved path due to a perpendicular force (F = mv2 / r is not required).
定性的描述物体在一个垂直力的作用下沿曲线运动。
(b) Turning effect 转动效果
5. Describe the moment of a force as a measure of its turning effect and give everyday examples. 描述力矩是力的转动效果量度并且取例子。
6. Describe, qualitatively, the balancing of a beam about a pivot.
定性的描述一个杆关于支点的平衡。
15. Perform and describe an experiment (involving vertical forces) to verify that there is no net moment on a body in equilibrium.
演示和描述一个实验证明物体在合力矩为零时会保持平衡。
16. Apply the idea of opposing moments to simple systems in equilibrium.
应用反向的力矩简化一个系统的平衡。
(c) Conditions for equilibrium 平衡的条件
7. State that, when there is no resultant force and no resultant turning effect, a system is in equilibrium. 描述当合力为零并且合力矩为零时,系统保持平衡。
(d) Centre of mass 质心
8. Perform and describe an experiment to determine the position of the centre of mass of a plane lamina. 演示和描述一个在几何平面内找出物体质心的实验。
9. Describe qualitatively the effect of the position of the centre of mass on the stability of simple objects. 定性的描述质心的位置对物体稳定的影响。
(e) Scalars and vectors 标量和矢量
17. Demonstrate an understanding of the difference between scalars and vectors and give common examples. 阐明和理解标量和矢量之间的区别并且提出常见的例子。
18. Add vectors by graphical representation to determine a resultant.
通过图像表示求两个矢量的和。
19. Determine graphically a resultant of two vectors.
通过画图求两个矢量的和
1.6 Energy, work and power 能量,功和功率
(a) Energy能量
1. Demonstrate an understanding that an object may have energy due to its motion or its position, and that energy may be transferred and stored.
描述和理解一个物体由于运动和位置产生的能量,这个能量能够被转换和储存。
2. Give examples of energy in different forms, including kinetic, gravitational, chemical, strain, nuclear, internal, electrical, light and sound.
给一些不同形式的能量的例子,包括动能,势能,化学能,弹性势能,核能,内能,电能,光能和声能,
3. Give examples of the conversion of energy from one form to another and of its transfer from on place to another.
给一些从一种形式的能量转换为另一种形式的能量,从一个地方传播到另一个地方。
4. Apply the principle of energy conservation to simple examples
应用能量守恒的简单的例子。
8. Recall and use the expressions k.e.= ½ mv2 and p.e. = mgh
记住和应用表达式K.e=1/2mv和p.e=mgh
(b) Energy resources 能源
5. Describe how electricity or other useful forms of energy may be obtained from
(i) chemical energy stored in fuel
(ii) water, including the energy stored in waves, in tides, and in water behind hydroelectric dams
(iii) geothermal resources
(iv) nuclear fission
(v) heat and light from the Sun
描述电能和其它有用的能量形式怎样从下列能源获得的:
(i) 储存在然连中的化学能。
(ii) 水包括储存在波和潮汐中的能量和水力电气水坝后面的水里面的重力势能
(iii) 地热能
(iv) 核裂变
(v) 来自太阳的热和光能
9. Show an understanding that energy is released by nuclear fusion in the Sun.
描述和理解太阳的核裂变释放能量
10. Show a qualitative understanding of efficiency 定性的理解效率
(c) Work 功
4-relate, without calculation, work done to the magnitude of a force and the distance moved不通过计算找出做功与力的大小和移动的路程之间的关系
5-describe energy changes in terms of work done
描述能量的改变就是做功
6-recall and use ΔW = Fd = ΔE记住和应用
(d) Power 功率
1-relate, without calculation, power to work done and time taken, using appropriate examples不用计算用合适的例子找出功率与做功和时间的关系
2-recall and use the equation P = E/t in simple systems
记住和应用在一个简单的系统P=E/t
1.7 Pressure压强
1-relate, without calculation, pressure to force and area, using appropriate examples
不通过计算,通过合适的例子得出压强,力和面积之间的联系
2-describe the simple mercury barometer and its use in measuring atmospheric pressure描述简单的水银气压计和用它来测量大气压强
3-relate, without calculation, the pressure beneath a liquid surface to depth and to density, using appropriate examples
不通过计算通过合适的例子得出液体表面下的压强,升读和密度之间的关系
4-use and describe the use of a manometer描述压力计的应用
5recall and use the equation p = F/A记住,会用等式P=F/A
6-recall and use the equation p = hρg记住会用等式p=pgh
GCSE物理考试注意事项
2019年的考官报告显示:
对于图表题目,解答时描述太简单。没有考虑图表形状的曲线变化;许多学员难以把曲线变化与实际上发生的变化相联系
单位换算做得不好。如tera-和milli-
物理词汇的混淆。比如,Precision与accuracy/resolution混淆
电磁学没有被很好地理解
混淆了宇宙大爆炸的天体的生命周期
审题错误。不使用题目中给出的数值,而是使用常规数值进行计算
所以大家复习GCSE物理考试和答题的时候要针对以上问题进行训练哦。
希望以上内容可以帮到你的GCSE物理考试。时值3月下旬,冲刺倒计时已开启,大家一定要把握住仅剩的时间认真学习,把自己的薄弱环节及时补上去。如果现在的你离目标分还需加把劲,或者感到来不及复习多门选课,点击预约试听【唯寻IGCSE复习冲刺班】——
全球海归授课,
高效攻克薄弱环节,
迅速掌握重要知识点的学习方法,
开阔学习思路,
无论考试规则怎样变化,
都能脚踏实地冲A*/9分。
优秀的IGCSE / GCSE成绩是不仅是学好A-level的基础,更是进入英国知名大学的标配,近年来英国牛津剑桥都会要求学员在IGCSE考试中获得5个A或A*,所以IG阶段的复习也是非常关键的。
更多IGCSE / GCSE学习攻略点击











































 沪公网安备 31010502004453号
沪公网安备 31010502004453号





 成功提交后我们将尽快与您联系,请注意来电!
成功提交后我们将尽快与您联系,请注意来电!





 成功提交后我们将尽快与您联系,请注意来电!
成功提交后我们将尽快与您联系,请注意来电!