呼吸作用是Alevel生物中的一个重要考点,对于这个知识点还不理解的同学不妨跟我们一起来重新梳理一下这部分的知识点吧。赶紧来收下这份Alevel生物呼吸作用知识点吧!

呼吸作用简化的形式,是由一个单一的方程表达的:

但呼吸作用实际上是由四个复杂过程组成的,A2之后就不能用这样过分简化的表达式了,不过我们从这个表达式中可以看出来,呼吸作用需要氧气和分解底物(Substrate),通常是葡萄糖(Glucose),完全分解得到水,二氧化碳和大量能量。
Definition: Respiration is the chemical process of releasing energy from organic compounds.
Gas exchange - The movement of oxygen into an organism and carbon dioxide out of an organism.
Breathing - The ventilation movements that are needed in some larger animals so that efficient gas exchange can take place. It involves ribs, intercostal muscles, the diaphragm and lungs.
Respiration - The process by which complex organic molecules are broken down to release energy.
Aerobic respiration - Requires oxygen to fully oxidise the organic molecule. This releases lots of energy.
Anaerobic respiration -The breakdown of the molecule without oxygen. This releases much less energy.
气体交换是物理运动,气体分子的进出;呼吸运动指的是两个肺叶舒张收缩引起内外气压差,导致气体流入和流出的过程;呼吸作用指的是分解有机物释放能量的复杂化学变化;然后呼吸作用又分为有氧呼吸和无氧呼吸。
e.g. Outline the need for energy in living organism using named examples(9)
这道题要描述生物如何利用能量,并写出例子,分值有九分。
Here’s my answer example:
1.For active transport——K+—Na+ pump (钠钾泵主要控制神经系统调解,这个在内稳态homeostasis里会详细介绍)
2.Mechanical movement——muscle contraction, cilia movement, flagella movement(肌肉收缩,小肠绒毛蠕动,细菌鞭毛运动都是需要能量的)
3.Maintain body temperature(for mammals and birds恒温动物散热维持体温)
4.Synthesis complex substances from simpler ones—— nuclear acids from nucleotides, polysaccharides from monosaccharide, lipid synthesis, amino acids
5.Bioluminescence and electrical discharge(这个书上没有给例子,就说了某些微生物,其实主要有群聚效应的发光细菌)
Overlook of four stages of respiration:
呼吸作用分为有氧呼吸和无氧呼吸。
根据CIE考纲,有氧呼吸有四个阶段:Glycolysis (splitting of sugar)——Krebs cycle——Electron transport chain(ETC)——Oxidative phosphorylation
无氧呼吸就只有Glycolysis 一个阶段,因此无氧呼吸(Anaerobic respiration)的特点是速度快,适用于短时间内释放需要能量,比如短跑。
Why so many steps in respiration?
·Control harness all available energy at one instant
·Control by feedback mechanism (在内稳态章节会学到,只有negative feed back是有效的机制)
Structure of ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
What is ATP? ——ATP is the universal currency of energy. It is a small molecule with 3 phosphate groups (P) attached to an adenosine molecule i.e. Adenosine-P-P-P.
ATP是分子间的能量通货,堪比黄金在国际市场上的地位
ATP分子的结构是由一个五碳糖(ribose),一个nitrogen-containing base (adenine is a double ringpurine),和三个phosphate groups组成的,一个核糖和一个A组成adnosine.
During respiration, high energy C-C, C-H and C-OH bonds are broken. Lower energy bonds are formed and the difference is released and used to attach a P to Adenosine-P-P (ADP adenosine diphosphate), making ATP
ATP水解(hydrolysis)释放出大量能量(30.5KJ/mol),生成ADP
When energy is required at a later time by a cell, it can use the ATP and break a P off the end. This releases the energy needed (30.5kJ for every ATP, ADP + P). The more ATPs used, the more energy is released.
For aerobic respiration to occur, the cell needs to possess mitochondria.
线粒体结构的适应性有时候也会考,最明显的就是内膜(Inner membrane of mitochondria or cristae )增大表面积(Surface area)从而起到促进反应快速进行(Increase reaction rate)的作用;然后线粒体有独立的ribosome和DNA,能独立制造蛋白质(Transcription & translation)。
如果你想让ALEVEL生物或其他科目成绩更上一层楼,可以点击预约试听【唯寻ALEVEL复习冲刺班】,海归精准教学,根据不同考试局整理高频考察点,高效攻克薄弱环节,培养稳定A*/A实力,早日达到目标大学要求的分数线。
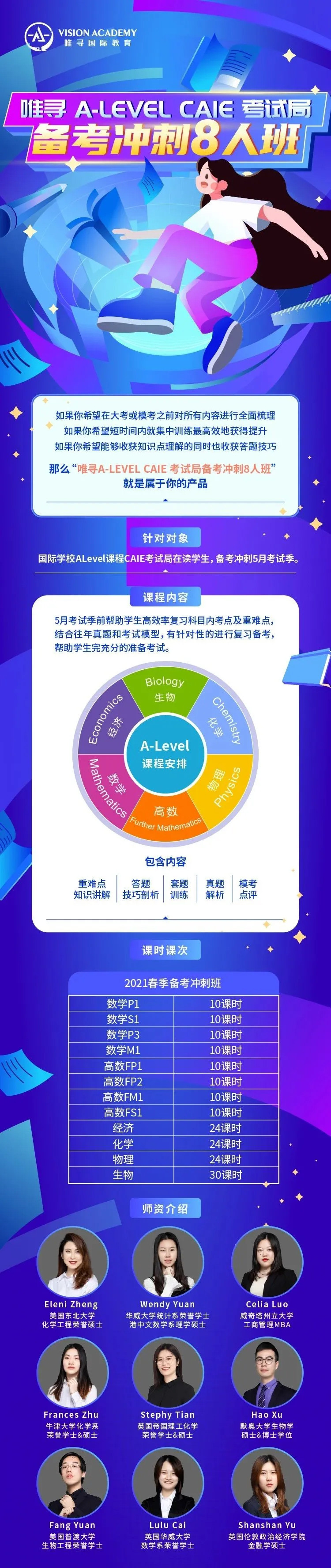
点击
查看。

学习有方法,成长看得见
筑梦牛剑/G5/常春藤