IGCSE经济的考试有很多题目就单纯地考概念本身,如果目标A*的话,这种相对好拿的分同学们要尽量一分都不丢。本文就为大家梳理一下IGCSE经济真题中出现过的定义,不要错过前辈留给你复习经验,拿去更高效地复习吧。

Basic economic problem: choice and the allocation of resources
1. Scarcity: asituation where there is not enough to satisfy everyone’s wants.
2. The economicproblem: unlimited wants exceed scarce resources.
3. Factors ofproduction: the economic resources of capital, enterprise, labour and land.
4. Land: gifts ofnature available for production.
5. Labour: allhuman effort mental and physical involved in producing goods and services.
6. Enterprise; riskbearing and decision making in business.
7. Occupationallymobile: capable of changing use.
8. Geographicallyimmobile: incapable of moving from one location to another location.
9. Capital: humanmade goods used in production.
10.Investment: spending on capital goods.
11.Depreciation: the value of replacing capital.
12.Productivity: output per worker hour.
13.Opportunity cost: the next best alternative forgone.
14.Economic good: a product which requires resourcesto produce it and therefore has an opportunity cost.
15.Free good: a product which does not requireresources to produce it and therefore has an opportunity cost.
16.Production possibility curve: a curve that showsthe maximum output of two types of products and combination of those productsthat can be produced with existing resources and technology.
17.A planned economy: an economy where the governmentmakes the crucial decisions, land and capital are state-owned and resources areallocated by directives.
18.A market economy: an economy where consumersdetermine what is produced, resources are allocated by the price mechanism andland and capital are privately owned.
19.A mixed economy: an economy in which both theprivate and public sectors play an important role.

The allocation of resources: how the market works; market failure
1. Demand: thewillingness and ability to buy a product.
2. Market demand:total demand for a product.
3. An extension indemand: a rise in the quantity demanded caused by a fall in the price of theproduct itself.
4. A contraction indemand: a fall in the quantity demanded caused by a rise in the price of theproduct itself.
5. Supply: thewillingness and ability to sell a product.
6. Market supply:total supply of the product.
7. An extension insupply: a rise in the quantity supplied caused by a rise in the price of theproduct itself.
8. A contraction insupply: a fall in the quantity supplied caused by a fall in the price of theproduct itself.
9. Equilibriumprice: the price where demand and supply are equal.
10.Disequilibrium: a situation where demand and supplyare not equal.
11.Changes in demand: shifts in the demand curve.
12.An increase in demand: a rise in demand at anygiven price, causing the demand curve to shift to the right.
13.A decrease in demand: a fall in demand at any givenprice, causing the demand curve to shift to the left.
14.Disposable income: Income after income tax andnational insurance contributions have been deducted.
15.Normal good: a product whose demand increases whenincome increases and decreases when income falls.
16.Inferior good: a product whose demand decreaseswhen income increases and increases when income falls.
17.Substitute: a product that can be used in place ofanother.
18.Compliment: a product that is used in conjunctionwith another product.
19.Ageing population: an increase in the average ageof the population.
20.Birth rate: the number of life birth per thousandof the population in a year.
21.An increase in supply: a rise in supply at anygiven price, causing the supply curve to shift to the right.
22.A decrease in supply: a fall in supply at any givenprice causing the supply curve to shift to the left.
23.Changes in supply: changes in supply conditionscausing shifts in the supply curve.
24.Unit cost: the average cost of production. It isfound by dividing total cost by output.
25.Improvements in technology: advances in the qualityof capital goods and methods of production.
26.A tax: a payment to the government.
27.Indirect taxes: taxes on goods and services.
28.A subsidy: a payment by a government to encouragethe production or consumption of a product.
29.Price elasticity of demand: a measure of theresponsiveness of demand to a change in price.
30.Private costs: costs borne by those directlyconsuming or producing a product.
31.Private benefits: benefits received by those directlyconsuming or producing a product.
32.External costs: costs imposed on those who are notinvolved in the consumption and production activities of others directly.
33.External benefits: benefits enjoyed by those whoare not involved in the consumption and production activities of othersdirectly.
34.Social costs: the total costs to a society of aneconomic activity.
35.Social benefits: the total benefits to a society ofan economic activity.
36.Cost benefits analysis: a method of assessinginvestment projects which takes into account, social costs and benefits.
希望以上IGCSE经济真题出现过的定义可以帮助你精准定位考点。
秋季IGCSE已然出分完毕了,距离今年IGCSE经济考试还有不到半年的时间,想要取得理想的成绩,复习可是从现在就要开始了。如果你还没有找到复习方法,或者陷于缺乏论文答题思路等细节问题,点击预约试听【IGCSE / GCSEwinter vacation培训班】——
唯寻教学天团授课,
带你完美过渡课程适应期,
高效率梳理知识点,
根据不同考试局整理高频考点,
考试技巧和国际课程基础两手抓,
用一个winter vacation的时间,
赶超大神、进阶学神
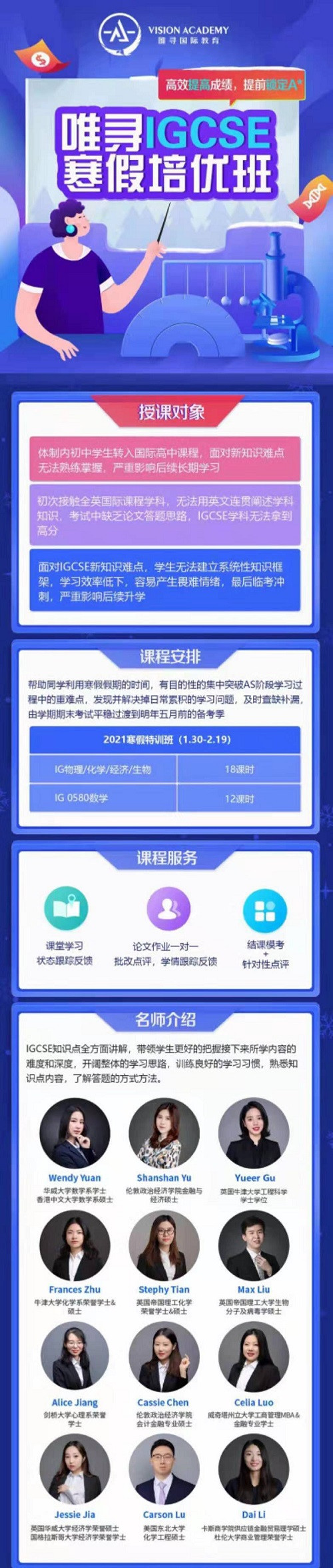
优秀的IGCSE/GCSE成绩是不仅是学好A-level的基础,更是进入英国优质大学的标配,近年来英国牛津剑桥都会要求学员在IGCSE考试中获得5个A或A*,所以IG阶段的复习也是至关重要的。
更多IGCSE/GCSE学习攻略点击

学习有方法,成长看得见
筑梦牛剑/G5/常春藤