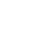
在AP美国史有很多重要的知识点,下面给大家讲的是AP美国史最高法院的裁决有关的知识点,这部分可是同学们考试的重点,一起来看看都有哪些考点吧!

Marbury v. Madison(1803)
This case established the Supreme Court’s power of judicial review—the power to determine whether or not a law or other government action is constitutional. This power has become part of the “unwritten Constitution” and one of the Supreme Court’s most important roles.
Gibbons v. Ogden(1824)
The court decided that the power to regulate interstate commerce, granted to Congress by the Commerce Clause of the United States Constitution, encompassed the power to regulate navigation.
美国是由独立的各州联邦组成的国家,因此联邦制使各州拥有广泛的权力。管理州内的工商业的权利在每个州自己的手里,但管理州与州之间的经济活动(interstate commerce)的权利却不得不让渡给联邦政府。因此美国宪法规定了管理对外贸易、州际贸易和与印第安部落的贸易是属于联邦政府的权利。但纸上的规定要化为实践还需要一个过程,而此案就促进了这个法律的落实。
Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857)
Dred Scott, an enslaved man of "the negro African race" who had been taken by his owners to free states and territories, attempted to sue for his freedom. The Supreme Court denied Scott's request, and held that "a negro, whose ancestors were imported into [the U.S.], and sold as slaves",whether enslaved or free, could not be an American citizen and therefore had no standing to sue in federal court, and that the federal government had no power to regulate slavery in the federal territories acquired after the creation of the United States.
此案的判决严重损害了美国最高法院的威望,更成为南北战争的关键起因之一。
Plessy v. Ferguson (1896)
This case gave the legal green light to “separate but equal” public facilities for blacks and whites. It legitimized the Jim Crow segregation laws that would characterize racial policy for the next half-century.
对此案的裁决标志着“隔离但平等”原则的确立。最高法院裁定“隔离但平等”并不意味着对黑人的歧视,而只是确认白人和黑人之间由于肤色不同而形成差别。该案的裁决事实上确认了种族隔离政策的合法性,直到1954年的 Brown v. Board of Education,这一政策方才失去其合法地位。
Korematsu v. US(1944)
The Supreme Court upheld the constitutionality of detention camps for Japanese-Americans during World War 2.
第二次世界大战期间美国最高法院判决认定强制日裔美国人从太平洋沿岸地区迁移的命令为合宪。这一判决在后来成为了美国最高法院史上最为人抨击的判决之一。
Brown v. Board of Education(1954)
Essentially undoing Plessy v. Ferguson, the Supreme Court ruled that “separate but equal” facilities for blacks and whites were “inherently unequal.” This case outlawed racial segregation of public schools and paved the way for the integration of other areas as well.
此案判决种族隔离本质上就是一种不平等,因此种族隔离的法律因为剥夺了黑人学童的入学权利而违反了the 14th Admendments所保障的平等权而违宪。此案终止了美国社会中存在已久白人和黑人必须分别就读不同公立学校的种族隔离现象。从本判决后「隔离但平等」的法律原则被推翻,从此美国开始废止一切有关种族隔离的措施,民权运动和种族融合也因为本案迈进一大步。

Gideon v. Wainwright (1963)
This decision expanded the guarantees of the Bill of Rights by ruling that the 6th Amendment right to an attorney regardless of ability to pay applies to state cases as well as federal ones.
此案裁决,获得律师帮助权属于公平审判的最基本内容,应当纳入宪法第14条修正案中“正当法律程序”的保护之列。
Miranda v. Arizona (1966)
This case is designed to make sure that those accused of a crime know their rights before they are interrogated by police. This is known as the “Miranda Warning” or “Miranda Rights.”
在这个判决中,联邦最高法院规定在实施逮捕和审讯嫌犯时,警方必须及时提醒嫌犯有权保持沉默,拒绝回答警方提出的问题;
如果回答了警方的问题,这些供词将会用来起诉和审判他们;
可以请律师,并且可以要求审问时有律师在场给予帮助;
如果他请不起律师,法庭将免费为之指派一位。因为这个判决,米兰达警告沿用至今。
Roe v. Wade(1973)
The Supreme Court used the 4th Amendment as the basis to legalize first trimester abortion.
美国联邦最高法院承认妇女的堕胎权受到宪法隐私权的保护。
US v. Richard Nixon (1976)
This case resulted in a unanimous decision against President Richard Nixon, ordering him to deliver tape recordings and other subpoenaed materials to a federal district court. The decision was important to the late stages of the Watergate scandal, when there was an ongoing impeachment process against Richard Nixon. United States v. Nixon is considered a crucial precedent limiting the power of any U.S. president to claim executive privilege.
此案判决命令时任美国总统理查德·尼克松交出特别检察官要求的白宫录音带。这一判决对水门事件产生了重要的影响,判决仅半个月后,尼克松宣布辞职。这一案件也被认为是对美国总统权力作出限制的一个关键性的判决先例。
以上就是今天给大家带来的一些有关AP美国史最高法院的裁决的信息了,同学们已经迎来考试,如果您还有复习疑问或者复习计划准备不充分,欢迎您随时前来唯寻,我们有专业的导师来帮您知道制定属于您自己的复习方案。点击【预约试听】即可了解更多课程信息。
点击
AP美国史独立战争考点分享 复习美国史的你对于独立战争了解多少呢
AP美国史怎么考理想分? 考前背这份根据大纲总结出来的AP美国史复习重点就行了
查看。

学习有方法,成长看得见
筑梦牛剑/G5/常春藤